Earth Observation (EO) refers to the “gathering of information about planet Earth’s physical, chemical and biological systems, and involves monitoring and assessing the status of, and changes in, the natural and man-made environment,” according to the Group on Earth Observations (GEO), a voluntary global partnership of governments and international organizations that coordinate their strategies and create synergies to maximize the benefits of investments in EO.
In this frame, APCG operates the Greek GEO Office, the focal point of GEO activities in Greece, and develops symbiosis between the different EO platforms (i.e. satellites, in situ, models, citizen observatories), while at the same time pursuing the exploitation of European and international assets (e.g. Copernicus, GEOSS) to deliver added value services and products to citizens and stakeholders.
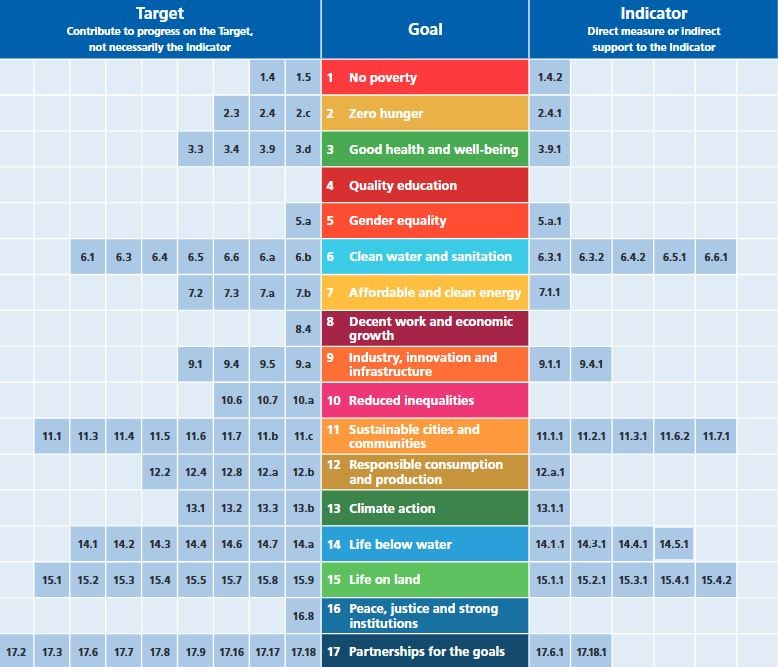 The Targets and Indicators of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which can be benefited from Earth Observation (EO) and geo-spatial information (Source: GEO EO4SDG: eo4sdg.org).
The Targets and Indicators of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which can be benefited from Earth Observation (EO) and geo-spatial information (Source: GEO EO4SDG: eo4sdg.org).
Our activities include:
Development of new methodologies and delivery of EO-based tools towards monitoring the UN 2030 Agenda Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) and selected indicators, in close collaboration with the GEO Secretariat, the EO4SDG Initiative and other competent national (e.g. NSO) and international entities (e.g. UNGGIM)
Geospatial analysis involving spatial modeling and statistics, utilization of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for the collection, control, processing, analysis and visualization of environmental and socio-economic data
Explicit focus on urban environmental stressors, with an emphasis on air quality, to address the science and policy challenges and identify mitigation opportunities that stem from the complexity of the urban environment and are high on the EU’s policy agenda (e.g. Urban Agenda for the EU)
Development and application of urban scale emission and air quality numerical tools over European cities.
Exploitation of the new Smart City paradigm, bridging of Smart city components such as Internet of Things (IoT), dynamic gathering and dissemination of information and personalized notifications with traditional and novel EO platforms and applications
Incorporation and coupling of socio-economic perspectives in traditional EO information layers, including urban growth, population attributes and dynamics, as well as other indicators to capture environmental feedbacks, address social inequalities, and include cost and efficient design of mitigation measures for urban pressures
Collaboration with decision makers and other stakeholders in a “co-design” approach across all implementation cycles, in pursuit of the smooth uptake of the new observational capacities such as citizen science, low-cost sensors, UAVs and other Key Enabling Technologies (KETs) in key policy frames
Education and training of the next generation of citizens and stakeholders on the benefits from the use of EO
Development of Nature based Solution (NbS) in the urban environment to confront climate change vulnerability, improve the adaptive capacity taking advantage of EO-based products and services.
Mapping, monitoring and assessment of ecosystem services using remote sensing tools to apply multiple methodological approach to investigate the biodiversity status, the carbon and water cycles and the energy balance of urban and rural ecosystems.
The establishment of the Urban Heritage Climate Observatory (UHCO), led by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) World Heritage Centre (WHC) and the Greek GEO Office (GGO), which provides a forum for relevant partners to share good practices, needs and expertise; matches user needs to EO assets to enrich and coordinate processes for the preservation, monitoring, management of urban heritage, as well as communication and advocacy around local, national and international Climate Action; and enables a modernization of practices through co-producing targeted tools and services focusing on climate change risks and impacts to urban heritage.